All AWS S3 buckets that support instant access, including Standard, Standard-IA, Intelligent-Tiering, and Glacier Instant Retrieval, are supported. Refer to AWS documentation for the differences between these storage types.
All data in transit to and from a storage node and at rest, stored in the Amazon S3 storage node, is encrypted. In addition, SSE-S3 encryption is automatically set on all S3 buckets. You can also use AWS Key Management Service (SSE-KMS) keys to further encrypt your data (SSE-KMS).
CTERA recommends that in order to keep the log clean of CloudWatch based errors and present the actual bucket usage, Amazon CloudWatch should be associated with the user creating the Amazon S3 storage node. You can configure the Amazon S3 srorage node to connect to AWS using an IAM Role Policy, by using the Use AWS IAM Role Policy for the connection. For an example IAM policy, see the instructions for Creating the IAM, Policy and Role for the Portal.
All data in transit to and from a storage node and at rest, stored in the Amazon S3 storage node, is encrypted. In addition, SSE-S3 encryption is automatically set on all S3 buckets. You can also use AWS Key Management Service (SSE-KMS) keys to further encrypt your data (SSE-KMS).
CTERA recommends that in order to keep the log clean of CloudWatch based errors, Amazon CloudWatch should be associated with the user creating the Amazon S3 storage node.
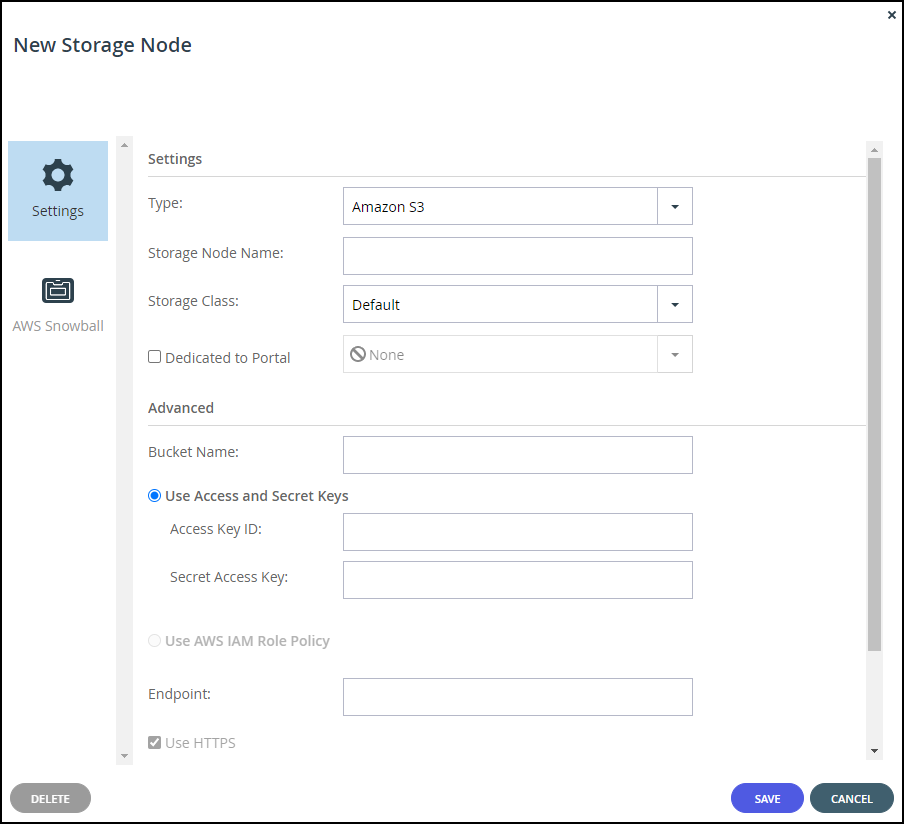
As soon as you specify that the storage node is Amazon S3, an AWS Snowball option is added to the New Storage Node window. For details, see Setting Up the CTERA Portal with AWS Snowball.
Bucket Name – A unique name for the Amazon S3 bucket that you want to add as a storage node.
Use Access and Secret Keys – Use Amazon S3 access credentials for the storage node.
- Access Key ID – The AWS S3 access key ID.
- Secret Access Key – The AWS S3 secret access key.
Use AWS IAM Role Policy – When the portal is also running as an AWS EC2 instance, you can define an IAM policy and then assign this policy to an EC2 role which is then attached to the portal instance, via Instance Settings > Attach/Replace IAM Role in the AWS Management Console. If you set up this type of policy, you do not need to specify the access and secret keys to access the storage node. For an example IAM policy, see the instructions for Creating the IAM, Policy and Role for the Portal.
Endpoint – The private endpoint name of the S3 service. The port for the endpoint can be customized by adding the port after the URL, using a colon (:) separator. The default port is 80.
Storage Nodes defined using the s3.amazonaws.com global endpoint are offline until the endpoint is changed to a private endpoint.
Use HTTPS – Use HTTPS to connect with the storage node.
- Trust all certificates – Do not validate the certificate of the object storage. Normally this is unchecked.
Direct Mode – Data is uploaded and downloaded directly to and from the storage node and not via the portal. If direct mode is defined for the storage node, CTERA recommends setting the deduplication method to fixed blocks and keeping the default 4MB fixed block size. For details, see Default Settings for New Folder Groups.
Once Direct Mode is set, the Use HTTPS option is also checked and cannot be unchecked.
Add Metadata Tags – Use metadata to support information lifecycle management rules (ILM) on the storage node to differentiate between backup and cloud drive blocks. Checking Add Metadata Tags implements the ILM, enabling storage tiering so that data can be routed across different object storages based on whether the data is backup or cloud drive related.