- 4 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Using AWS S3 Intelligent-Tiering For Storage
- 4 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Each object in Amazon S3 has an Amazon S3 storage class associated with it. Amazon S3 offers a range of S3 storage classes for the objects that you store. You choose a class depending on your use case scenario and performance access requirements.
The S3 Standard storage class is the default storage class if you don't specify a storage class when you upload an object to AWS. However, Amazon also offer a storage class that automatically optimizes frequently and infrequently accessed objects, the S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class.
The S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class is designed to optimize storage costs by automatically moving data to the most cost-effective storage access tier, without performance impact or operational overhead.
How Does S3 Intelligent-Tiering Work
The S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class is suitable for objects larger than 128 KB that you plan to store for at least 30 days. The storage class stores objects in two access tiers: one tier that is optimized for frequent access and another lower-cost tier that is optimized for infrequently accessed data. Amazon S3 monitors access patterns of the objects in the storage class and moves data on a granular object level that has not been accessed for 30 consecutive days to the infrequent access tier.
With intelligent tiering, you are charged a monthly monitoring and automation fee per object instead of retrieval fees. If an object in the infrequent access tier is accessed, it is automatically moved back to the frequent access tier, but no fees are applied when objects are moved between access tiers within the S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class.
The bigger the block size, the larger the savings. CTERA recommends using the S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class when the block size is set to 1MB or larger. If the block size is less than 1MB, contact CTERA support to see whether there is a saving. The larger the average object size the more negligible is the monitoring and automation fee as part of the whole fee. Whether you use intelligent tiering or not is mainly dependent on the following considerations:
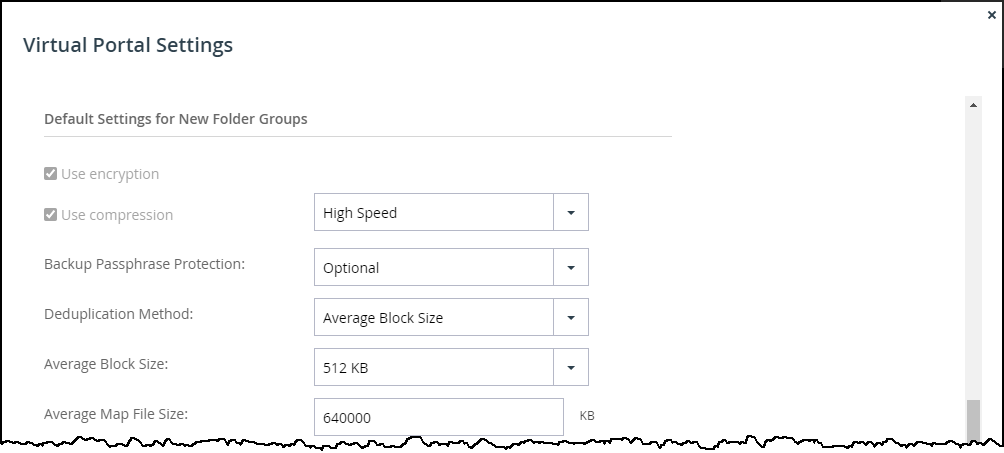
- The average block size of your objects. The S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class is suitable for objects larger than 128KB. In CTERA Portal files are broken down in to blocks and the block size is controlled by the Average Block Size setting in the Virtual Portal Settings. The default average block size is 512KB.Note
Use Fixed Block Size if direct mode is defined for the storage node and CTERA recommends keeping the default 4MB fixed block size.
CTERA Portal file maps are typically small and are not included in the intelligent tiering transition rule. - The percentage of infrequently accessed data.
- The percentage of objects stored for less than 30 days. The S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class is suitable for objects that you plan to store for at least 30 days and if you delete an object before the end of the 30-day minimum storage duration period, you are charged for 30 days. CTERA Portal retains deleted files for at least 30 days, to enable undeleting a file, meaning that this requirement can be ignored.
Changing Storage to S3 Intelligent-Tiering
Before transitioning storage to the S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class, CTERA recommends checking the average size of the objects being stored and the days they are held in storage.
When a version is defined for the bucket with a policy to rectify a ransomware attack, as described in Integrating CTERA Portal with S3-Versioned Buckets, the policy is transferred to the S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class.
To transition storage to intelligent tiering storage:
- From your Amazon Web Services account, sign in to the AWS Management Console and select Services.
- Under Storage select S3.
- Click the CTERA Portal bucket from the S3 buckets list and then select the Management tab.
The management details for the bucket are displayed. - Click Create lifecycle rule.
The Create lifecycle rule page is displayed. - Enter a name for the rule, make sure Limit the scope of this rule using one or more filters is chosen and in the Filter type prefix text box enter
blocks. - Under Lifecycle rule actions check Move current versions of objects between storage classes.
The page changes to display Transition current versions of objects between storage classes section. - For Choose storage class transitions select
Intelligent-Tieringand specify the number of days for the transition after the object is created. For example,7. - Review the details of the rule and if satisfied, click Create rule.
Lifecycle rules run once a day at midnight UTC.
The first time the rule runs, it can take up to 48 hours.
Use management metrics to validate the storage transition.
To access management metrics for an S3 bucket:
- From your Amazon Web Services account, sign in to the AWS Management Console and select Services.
- Under Storage, select S3.
- Click the CTERA Portal bucket from the S3 buckets list and then select the Metrics tab.
The metrics for the bucket are displayed. Graphs are displayed after transitioning to the S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class.


