Microsoft Sentinel is a cloud-based security information and event management (SIEM) platform that helps strengthen cyber-threat management and response systems. Microsoft Sentinel provides:
- Centralized and comprehensive visibility of all data across the entire IT infrastructure.
- AI-powered and automated threat detection that identifies, monitors, responds to and mitigates security risks in near-real time.
Using orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) capabilities, Microsoft Sentinel together with CTERA provides near-real-time threat intelligence and security analytics based on the data it collects and analyzes from across users, devices, applications and infrastructure. Microsoft Sentinel also automatically detects and responds to security threats and breaches.
You need CTERA Edge Filer 7.8.x or higher and CTERA Portal 8.2.x, and a Syslog server with both Azure Arc and Azure Monitoring Agent installed to be able to use Microsoft Sentinel.
How CTERA and Microsoft Sentinel work together
The integration between the CTERA Portal and Microsoft Sentinel is based on the logs it receives directly from the CTERA Portal via a Syslog server. The following enable security monitoring using CTERA Sentinel:
- CTERA Edge Filer SMB Audit Logs and CTERA Portal Logs
- Microsoft Sentinel Workbooks
- Microsoft Sentinel Analytics
- Microsoft Sentinel Hunting
- Viewing Incidents
CTERA Edge Filer SMB Audit Logs and CTERA Portal Logs
SMB audit logs are sent from different edge filers to the portal by the portal's Edge Filer Syslog service. From there, they are forwarded along with portal logs via a Syslog server to CTERA Sentinel installed in Microsoft Sentinel. Using CTERA Sentinel, these logs can be used for analysis and comprehensive security monitoring.
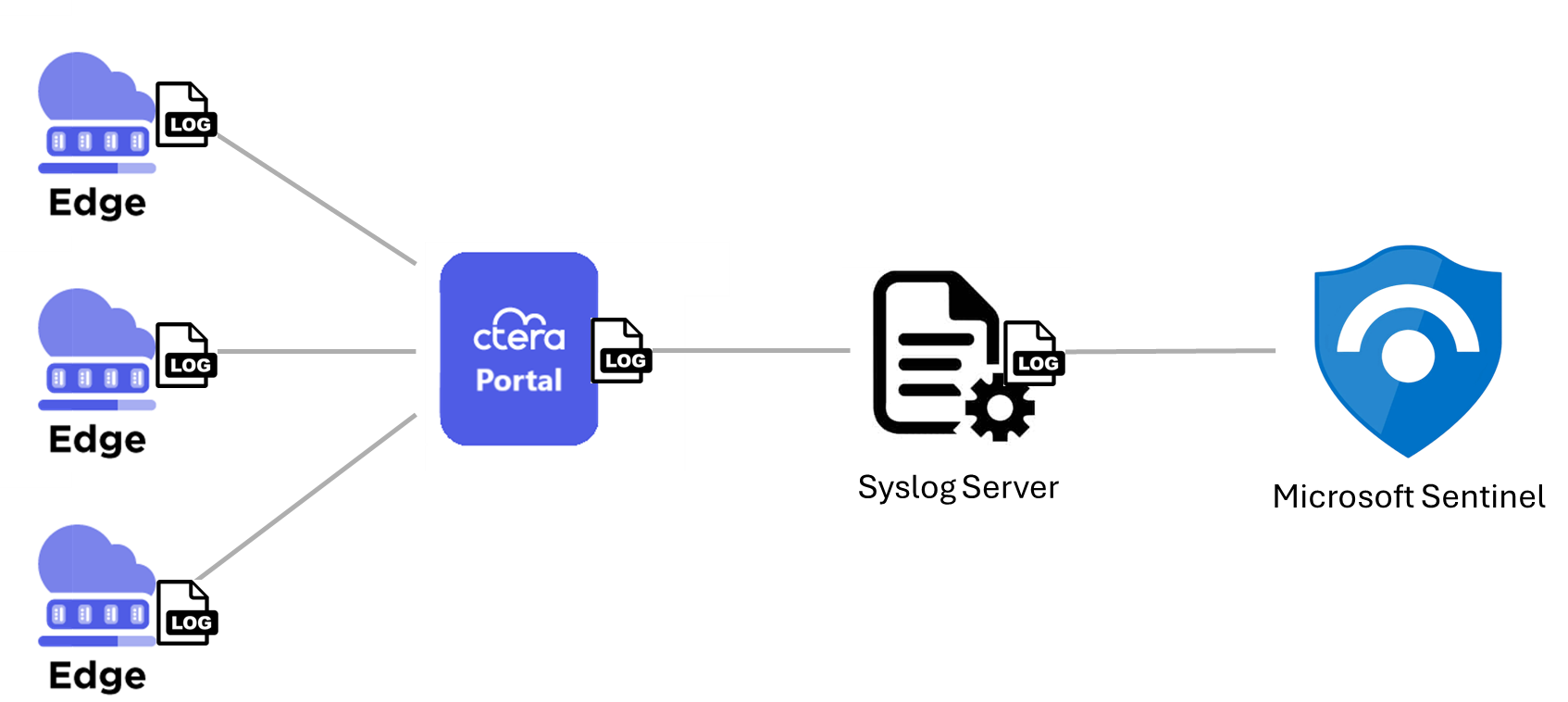
CTERA uses the Edge Filer Syslog service to gather all edge filer audit logs. For details see Managing the Edge Filer Syslog Service.
For details about how to connect the CTERA portal to a Syslog server, see
Setting Up Access to a Syslog Server.
Microsoft Sentinel Workbooks
Workbooks act as customizable dashboards to visualize, analyze and monitor your data. These workbooks allow you to add tables and charts with analytics for your logs and queries to make it easier to monitor key metrics and trends.
The CTERA Workbook displays relevant graphs and metrics for the CTERA workspace, including graphs of SMB audit logs. For example, the following CTERA Audit Logs Ingestion screen shows denied operations and deletion counts.
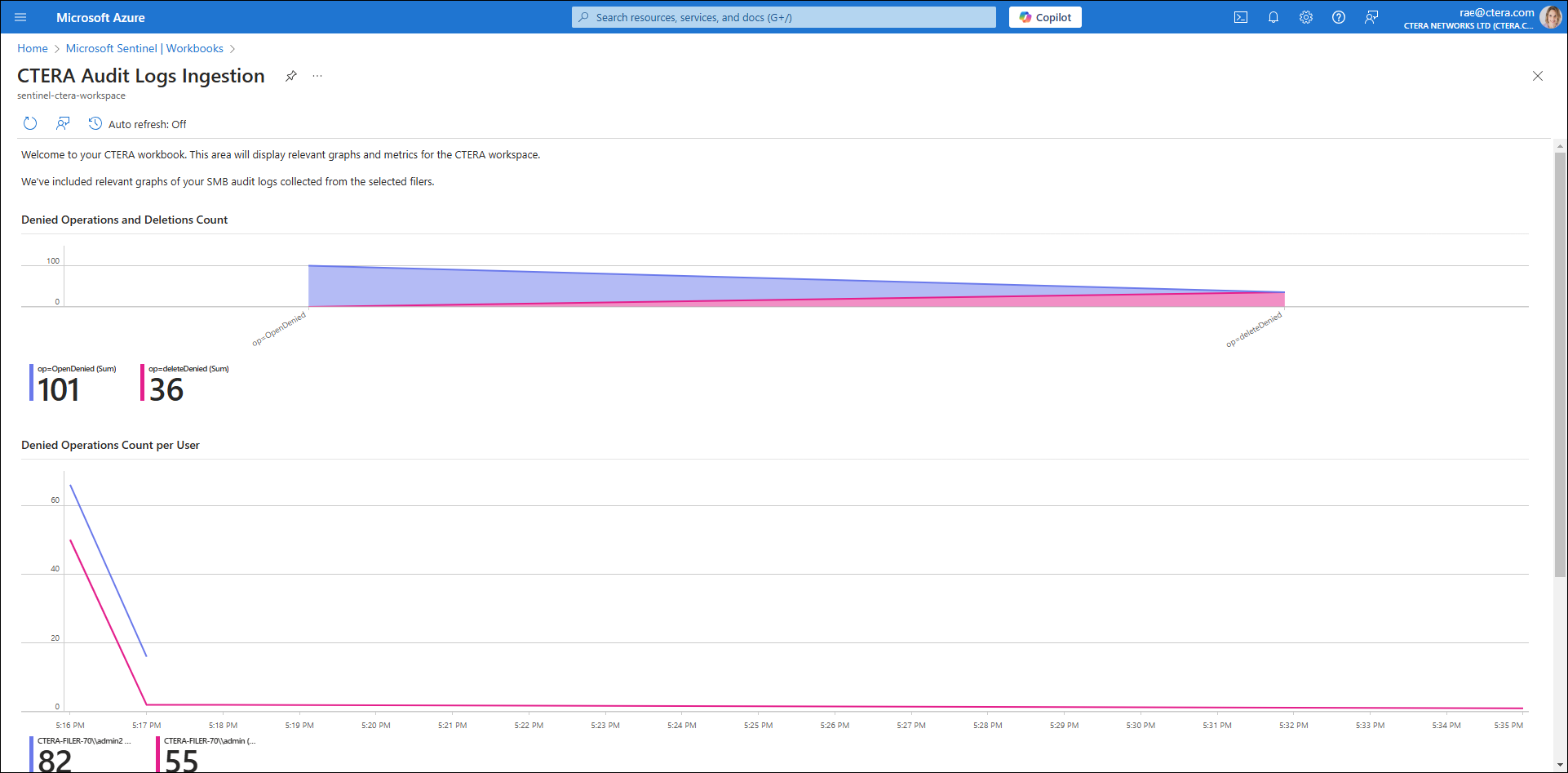
Graphs can also display details like denied operations per user and deleted operations per user.
Microsoft Sentinel Analytics
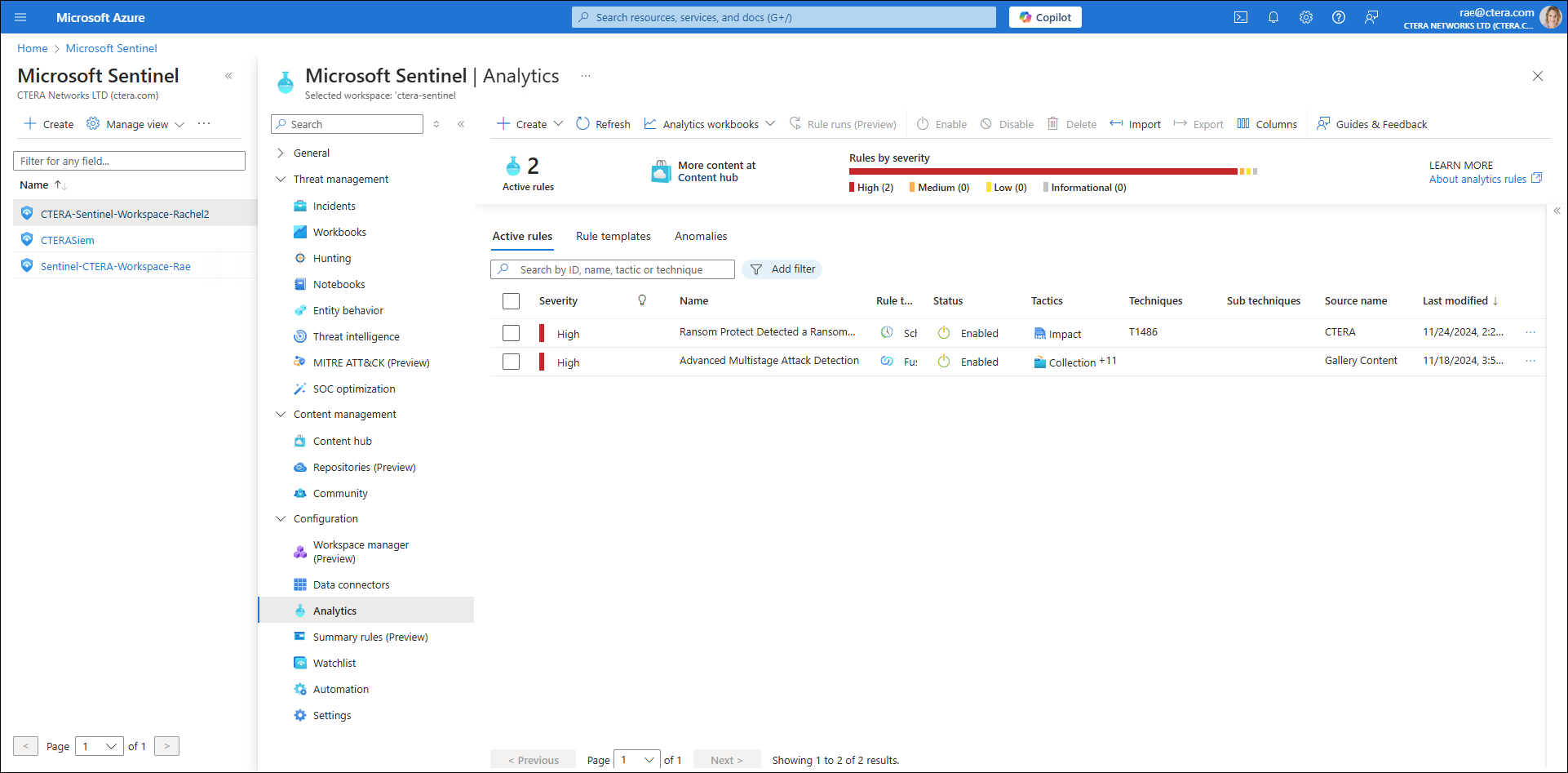
Analytics are predefined rules that constantly scan for patterns or anomalies in the data across your resources to automatically detect potential issues. When an analytics rule identifies potential security threats or suspicious events, it generates an alert containing details about the detected events. These may include the entities involved, such as users, devices, and addresses. These alerts are then aggregated and correlated into incidents, which can be investigated to determine the full scope of the detected threat in order to take appropriate action.
Analytics rules are scheduled to run every five minutes.
The following Analytics screen shows two active analytics rules that are designed for ransomware protection. These rules help detect and respond to potential ransomware activity.
The following table shows the collected metrics and alert creation for the CTERA Sentinel analytics rules:
| Alert Name | Monitored Events | More Information | Threshold | Technique/What is Done | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ransomware Detection | Portal log for detected ransomware attack | Monitors CTERA Ransom Protect for ransomware attacks | One ransomware event | 1486/Checks ability to encrypt data for negative impact | https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1486/ |
| Ransomware user blocked | Portal log for blocked user by ransom protect | Detects when CTERA Ransom Protect has blocked a user | One blocked malicious user | 1486/Checks ability to encrypt data for negative impact | https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1486/ |
| CTERA Mass Access Denied Detection | OpenDenied, createDenied, setsd, AclDenied, chown, deleteDenied | Detects access denied events | Generates an incident for 1000 access denied events within 5 minutes | 1562/Checks ability to impair defense mechanisms | https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1562/ |
| CTERA Mass Deletions Detection | delete | Detects file deletions | Generates an incident for 5000 deletions within 5 minutes | 1485/Checks malware designed to destroy data | https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1485/ |
| CTERA Mass Permission Changes Detection | ACLAdded, ACLDeleted, ACLProtectionAdded, ACLProtectionDelete, ACEChanged, setdacl | Detects permission changes | Generates an incident for 5000 permission denied events within 5 minutes | 1068/Checks ability to elevate privileges | https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1068/ |
| Antivirus Detected an Infected File | Portal log for infected files | Detects infected files | Generates an incident for each infected file event generated by edge filers | 1203/Checks for vulnerabilities in client applications | https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1203/ |
Microsoft Sentinel Hunting
Hunting is a tool that allows you to actively search for unusual behaviors or threats across your environment by running specific queries. These hunting queries are designed to catch suspicious activity before they becomes a bigger threat.
Hunting offers an extra layer of defense, giving you more control and insight into your data. The following queries are included by default in CTERA Sentinel:
CTERA Access Denied Detection – Tracks when a lot of access attempts are being blocked.
CTERA Batch Permission Changes Detection – Monitors for any unusual modifications to file and folder permissions.
CTERA Batch Deletions Detection – Scans for large-scale file deletions that could signal a problem.
The following table shows the collected metrics and thresholds for the hunting queries in CTERA Sentinel.
| Name | Monitored Events | More Information | Threshold | Technique/What is Done | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTERA Access Denied Detection | OpenDenied, createDenied, setsd, AclDenied, chown, deleteDenied | Detects access denied events | More than 10 access denied events in two minutes | 1562/Checks ability to impair defense mechanisms | https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1562/ |
| CTERA Batch Permission Changes Detection | ACLAdded, ACLDeleted, ACLProtectionAdded, ACLProtectionDelete, ACEChanged, setdacl | Detects permission changes | 100 permission changes in two minutes | 1068/Checks ability to elevate privileges | https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1068/ |
| CTERA Batch Deletions Detection | delete | Detects file deletions | 100 file deletions in two minutes | 1485/Checks malware designed to destroy data | https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1485/ |
Viewing Incidents
Microsoft Sentinel’s dashboard provides an overview of incidents flagged for review. They are categorized by severity, creation time, and whether they are new, active or closed. The dashboard also includes other data insights, analyses, and outcomes about threat management, content management and configuration.
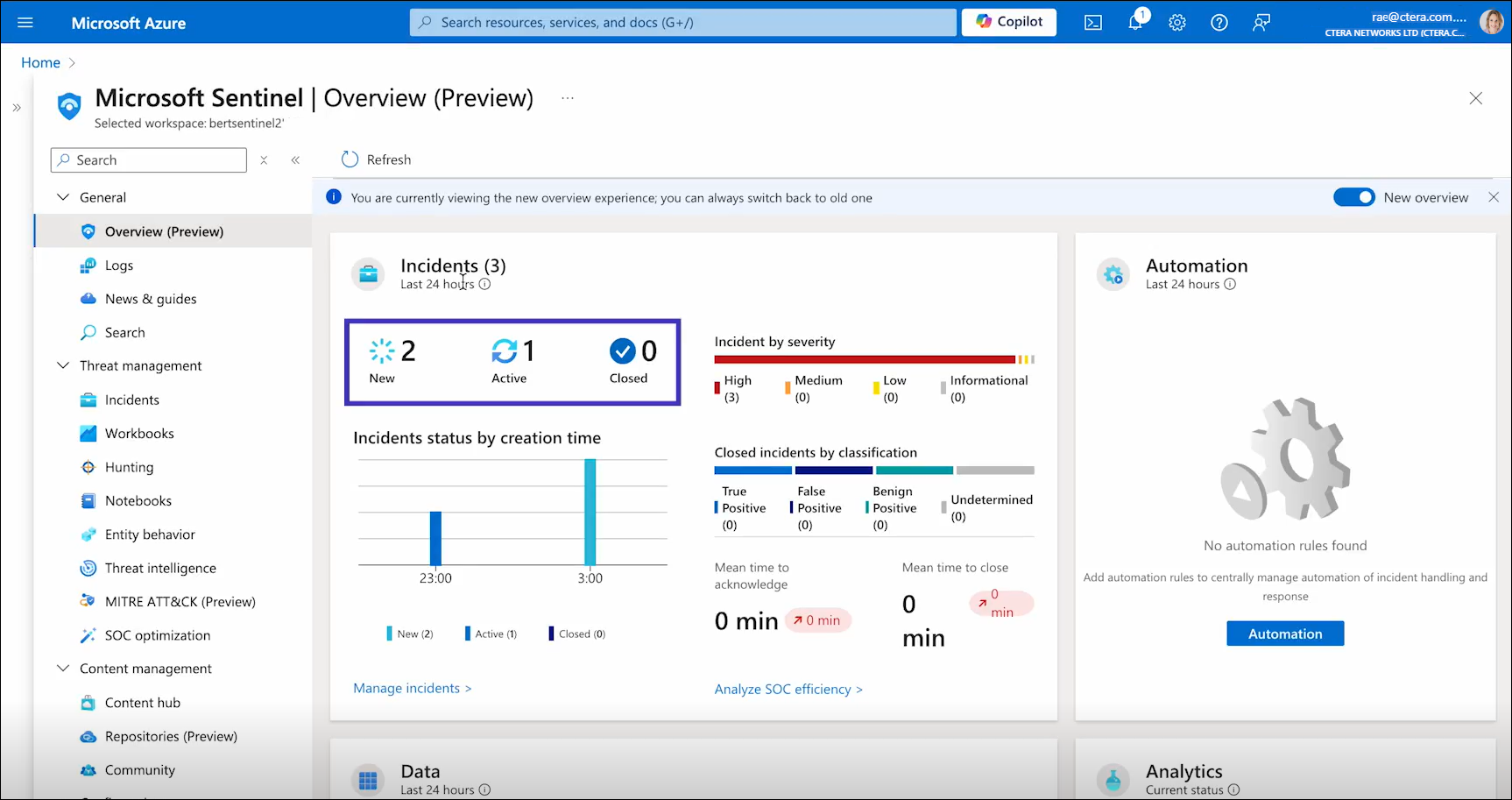
From the dashboard, you can navigate to the Incidents screen, for a more detailed view.
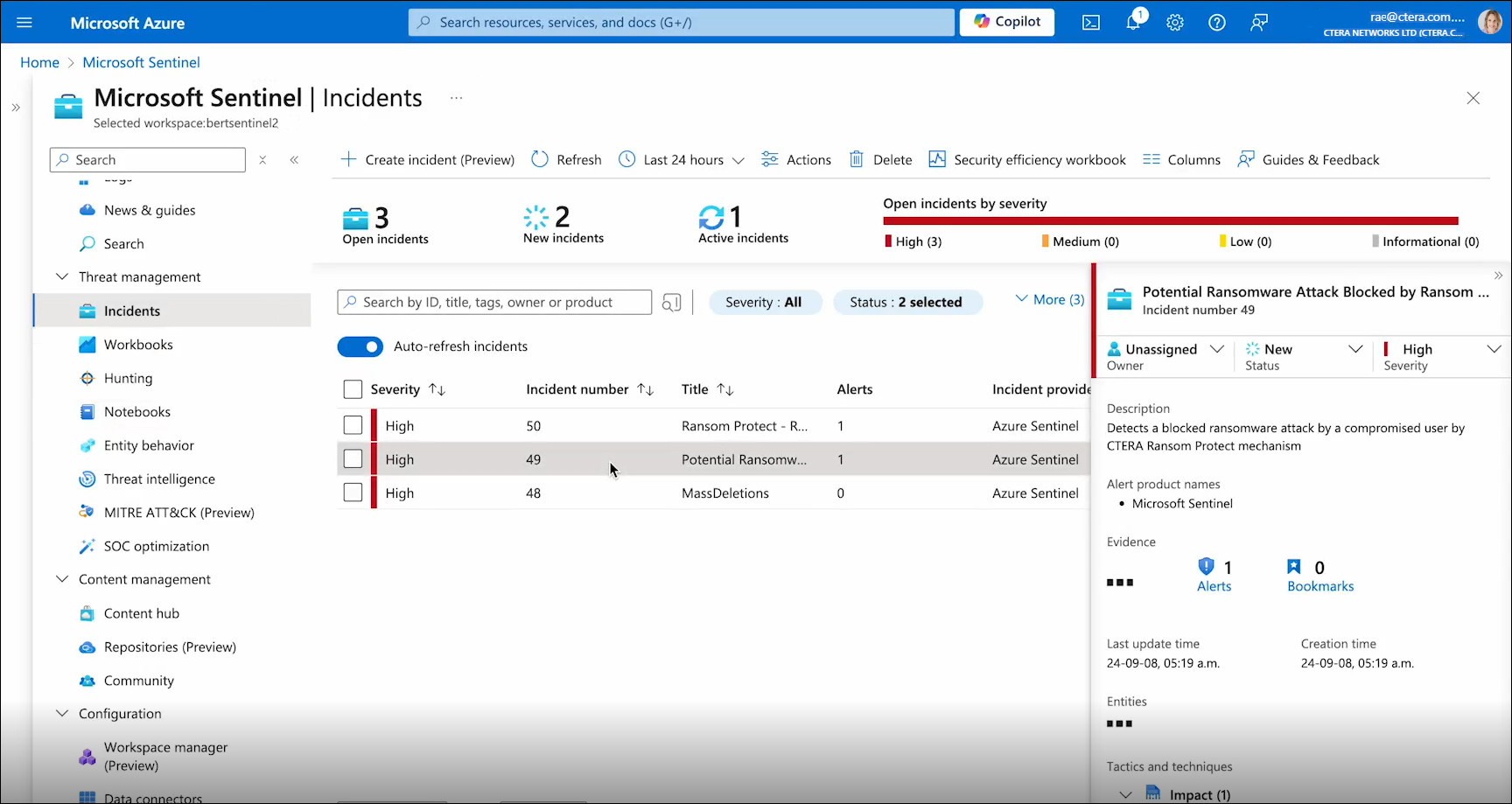
In the above example, one incident involves Mass Deletions while another one is for Ransomware Protection and a third confirms a Ransomware Attack.
Benefits of CTERA’s Integration with Microsoft Sentinel
CTERA’s integration with Microsoft Sentinel helps your threat management and response systems. Benefits include:
- A heightened level of visibility of data and threat intelligence. IT and security teams can include CTERA ransomware protection within their comprehensive enterprise-wide security monitoring.
- Near-real-time monitoring that enables rapid detection of and automated action against ransomware and other cyber threats.
- Automated and expedited incident response times to threats or breaches alleviate the workload on IT and security teams, enhancing their efficiency by enabling immediate action before further network infrastructures are affected.
- Ongoing cybersecurity defenses at scale, from local networks to remote, global offices. If a threat or breach occurs, instant alerts notify teams, wherever the location.